
|
How It Works!
|
|
|
What Is Infrared Heating? Infrared heating is the most efficient
and effective method in which to deliver "heat" under the diverse Hot gases are moved through the radiant tube either by vacuum (negative) or power
(positive) pressure. The radiant energy produced is then directed downward by the reflectors positioned above the radiant
tubes. |
||||||
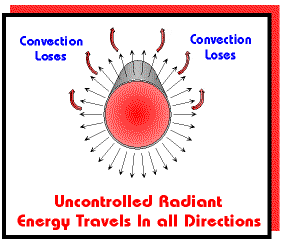

Reflectors positioned above the radiant tube direct the radiant
energy towards the floor area. The radiant energy is converted into heat when absorbed by objects in its path.
All of the radiant tubing network associated with both the OMEGA II® and Reflect-O-Ray® systems
are covered by reflectors -- including elbows and "U" bends. This important feature allows maximum radiant energy
efficiency.
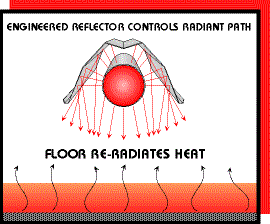
The infra-red energy is absorbed by the building's heat sinks, i.e. concrete floors, machinery, fixtures, etc. This heat sink is what in turn re-radiates energy for the "warmth" that is felt in the surrounding air. Because stratification of air (difference between floor temperature and ceiling temperature) is significantly lower than conventional hot, forced air systems, the structure heat loss is greatly reduced resulting in large savings in heating dollars.